##
## Bipolar disorder Healthy control
## Female 14 7
## Male 16 24
##
## Bipolar disorder Healthy control
## Female 22.95 11.48
## Male 26.23 39.34
##
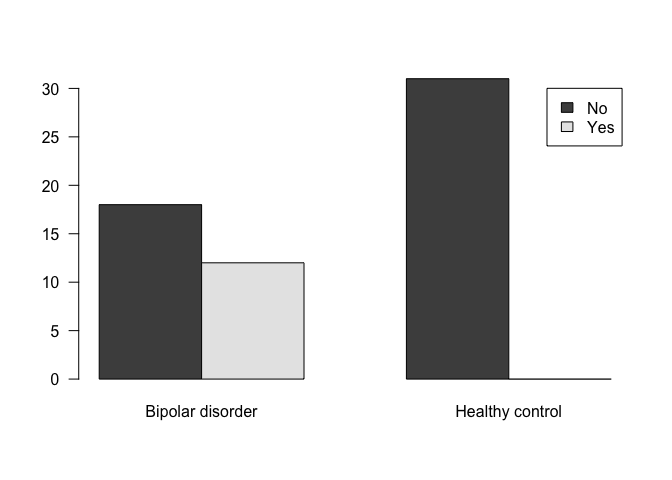
## Bipolar disorder Healthy control
## No 18 31
## Yes 12 0
# Create a basic function
mySummary <- function(myVar){
myMean = mean(myVar, na.rm = T)
myMedian = median(myVar, na.rm = T)
myIQR = IQR(myVar, na.rm = T)
mySd = sd(myVar, na.rm = T)
myVar = var(myVar, na.rm = T)
myCV = mySd/myMean * 100
Output = cbind(myMean, myMedian, myIQR, mySd, myVar, myCV)
return(Output)
}
Quantitative = data[,c(2:3,5,8,10,13,17:47)]
Result = apply(Quantitative,2,mySummary)
Quantitative = data[,c(2:3,5,8,10,13,17:47)]
Result_Male = subset(Quantitative, data$Gender == "Male") %>%
apply(.,2,mySummary)
Quantitative = data[,c(2:3,5,8,10,13,17:47)] %>% as.data.frame()
Out = list()
for(i in 1: ncol(Quantitative)){
myvector = Quantitative[,i] %>% as.numeric()
Out_tmp= by(myvector, data$Status, mySummary, simplify = T)
Out_tmp %<>% unlist %>% matrix(., nrow = 2, byrow = T) %>% as.data.frame()
names(Out_tmp) = c("mean", "median", "IQR", "sd", "Var", "CV")
rownames(Out_tmp) = c("Bipolar disorder", "Healthy control")
rownames(Out_tmp) = paste(names(Quantitative)[i], row.names(Out_tmp), sep = "_")
Out_tmp$Var = rownames(Out_tmp)
Out[[i]] = Out_tmp
}
Final = data.table::rbindlist(Out)
head(Final)
## mean median IQR sd Var CV
## 1: 44.533333 44.000 9.75 10.7084669 Age_death_Bipolar disorder 24.045959
## 2: 43.838710 45.000 10.50 7.3261940 Age_death_Healthy control 16.711701
## 3: 24.033333 22.000 9.50 7.9110718 Age_onset_Bipolar disorder 32.917081
## 4: NaN NA NA NA Age_onset_Healthy control NA
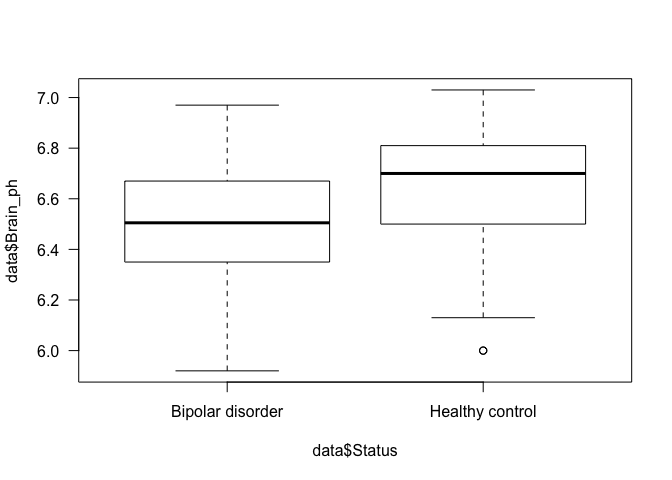
## 5: 6.475000 6.505 0.31 0.2743236 Brain_ph_Bipolar disorder 4.236658
## 6: 6.628387 6.700 0.31 0.2663844 Brain_ph_Healthy control 4.018842
##
## 1-sample proportions test with continuity correction
##
## data: ., null probability 0.5
## X-squared = 5.6333, df = 1, p-value = 0.01762
## alternative hypothesis: true p is not equal to 0.5
## 95 percent confidence interval:
## 0.5382722 0.8702456
## sample estimates:
## p
## 0.7333333
##
## 1-sample proportions test with continuity correction
##
## data: ., null probability 0.5
## X-squared = 2.7, df = 1, p-value = 0.1003
## alternative hypothesis: true p is not equal to 0.5
## 95 percent confidence interval:
## 0.4713741 0.8206242
## sample estimates:
## p
## 0.6666667
##
## 1-sample proportions test with continuity correction
##
## data: ., null probability 0.5
## X-squared = 20.833, df = 1, p-value = 5.01e-06
## alternative hypothesis: true p is not equal to 0.5
## 95 percent confidence interval:
## 0.7649271 0.9883682
## sample estimates:
## p
## 0.9333333
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: .
## W = 0.94384, p-value = 0.007419
## Warning in wilcox.test.default(x = c(6.6, 6.67, 6.7, 6.03, 6.35, 6.39, 6.51, :
## cannot compute exact p-value with ties
##
## Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
## data: data$Brain_ph by data$Status
## W = 303.5, p-value = 0.0201
## alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: .
## W = 0.94384, p-value = 0.007419
## Warning in wilcox.test.default(x = c(6.6, 6.7, 6.03, 6.39, 6.51, 6.5, 6.5, :
## cannot compute exact p-value with ties
##
## Wilcoxon rank sum test with continuity correction
##
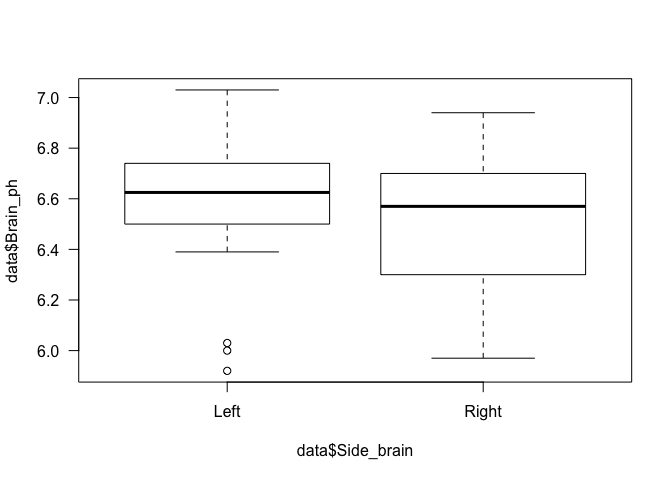
## data: data$Brain_ph by data$Side_brain
## W = 554, p-value = 0.1958
## alternative hypothesis: true location shift is not equal to 0
Genes = data[,17:ncol(data)]
myTest = function(myGene, myPhenotype){
myPhenotype %<>% as.factor()
myShap = myGene %>% shapiro.test()
if(myShap$p.value > 0.05){
myVar = var.test( myGene ~ myPhenotype)
if(myVar$p.value > 0.05){
myT = t.test(myGene ~ myPhenotype, var.equal = TRUE)
p = myT$p.value
}else if(myVar$p.value <= 0.05){
myT = t.test(myGene ~ myPhenotype, var.equal = FALSE)
p = myT$p.value
}
}
else if(myShap$p.value <= 0.05){
myT = wilcox.test(myGene ~ myPhenotype, paired = FALSE)
p = myT$p.value
}
return(p)
}
myTest(Genes$APOLD1, myPhenotype = data$Gender)
## Warning in wilcox.test.default(x = c(1.9942942989882, 2.05780061866762, : cannot
## compute exact p-value with ties
## APOLD1 CLDN10 DUSP4 EFEMP1 ETNPPL GJA1
## 5.317872e-01 7.263770e-01 8.863005e-01 7.319499e-01 1.757284e-01 4.555675e-01
## PLSCR4 SDC4 SLC14A1 SOX9 SST TAC1
## 2.678053e-01 1.348642e-01 3.858123e-01 2.524807e-01 1.397442e-02 5.619215e-01
## CX3CR1 DDX3Y ETNPPL.1 G3BP2 GABRG2 KDM5D
## 7.077235e-01 1.642534e-16 1.757284e-01 6.830784e-01 9.819888e-01 1.642534e-16
## MAFB NBEA OXR1 PAK1 PCDH8 PPID
## 1.806556e-01 2.416237e-01 5.824513e-01 5.317872e-01 2.416237e-01 3.775685e-01
## PVALB RPS4Y1 SST.1 TAC1.1 TBL1XR1 USP9Y
## 7.186072e-02 1.642534e-16 1.397442e-02 5.619215e-01 8.735223e-01 1.642534e-16
## XIST
## 1.642534e-16
## Warning in wilcox.test.default(x = c(2.1213099124647, 1.85484903769606, : cannot
## compute exact p-value with ties
## APOLD1 CLDN10 DUSP4 EFEMP1 ETNPPL GJA1
## 4.516246e-02 8.299889e-02 6.219081e-03 1.916905e-01 5.012671e-02 1.694804e-01
## PLSCR4 SDC4 SLC14A1 SOX9 SST TAC1
## 1.363228e-01 4.284287e-03 2.919839e-02 2.565146e-02 1.789292e-05 1.561385e-04
## CX3CR1 DDX3Y ETNPPL.1 G3BP2 GABRG2 KDM5D
## 3.469183e-02 4.516246e-02 5.012671e-02 2.664651e-03 1.982317e-02 1.080894e-01
## MAFB NBEA OXR1 PAK1 PCDH8 PPID
## 7.134286e-03 3.688796e-03 8.538568e-03 5.187831e-02 2.014827e-03 2.759478e-04
## PVALB RPS4Y1 SST.1 TAC1.1 TBL1XR1 USP9Y
## 4.694746e-03 2.246033e-01 1.789292e-05 1.561385e-04 9.682067e-03 2.062640e-02
## XIST
## 1.554616e-02
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
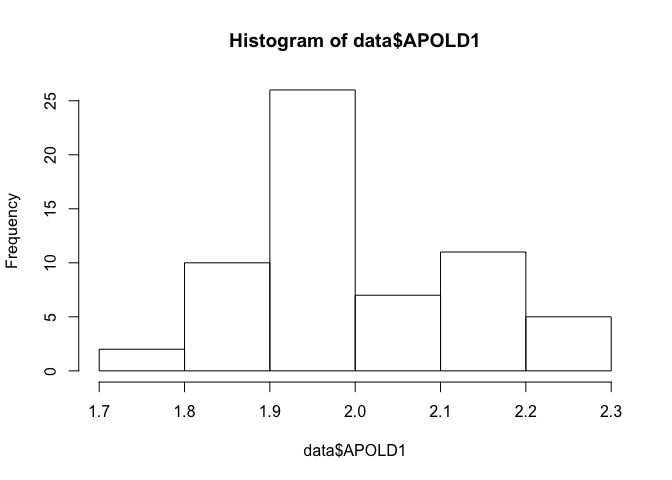
## data: data$APOLD1
## W = 0.95296, p-value = 0.01999
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
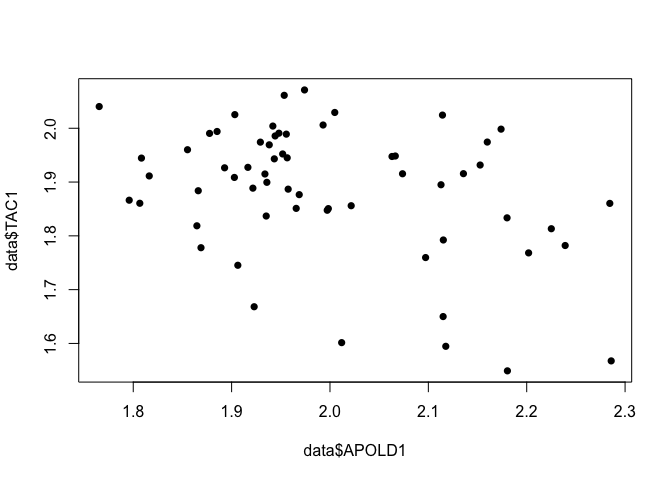
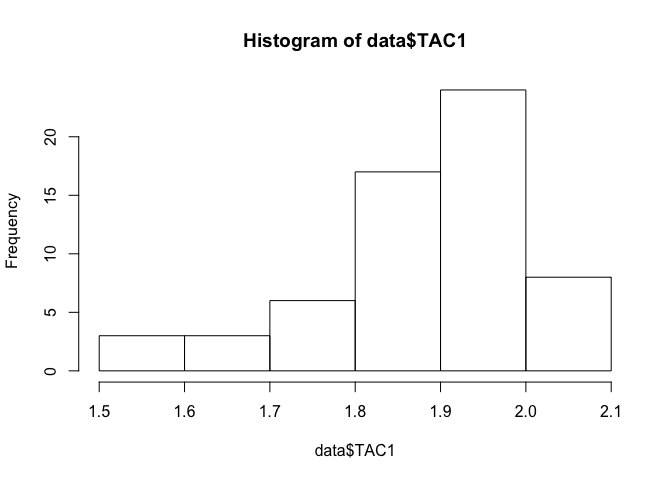
## data: data$TAC1
## W = 0.91607, p-value = 0.0004777
##
## No Yes
## No 15 3
## Yes 7 5
## Warning in chisq.test(.): Chi-squared approximation may be incorrect
##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test with Yates' continuity correction
##
## data: .
## X-squared = 1.2003, df = 1, p-value = 0.2733
##
## No Yes
## No 11 7
## Yes 9 3
## Warning in chisq.test(.): Chi-squared approximation may be incorrect
##
## Pearson's Chi-squared test with Yates' continuity correction
##
## data: .
## X-squared = 0.15625, df = 1, p-value = 0.6926
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: data$CLDN10
## W = 0.9634, p-value = 0.06516
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: data$EFEMP1
## W = 0.97247, p-value = 0.1846
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: data$PLSCR4
## W = 0.96814, p-value = 0.1125
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: data$SOX9
## W = 0.96446, p-value = 0.07367
##
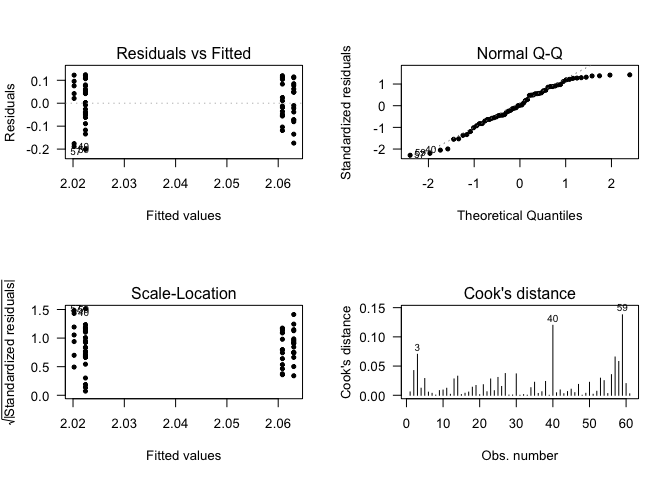
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$CLDN10 ~ data$Gender)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.217136 -0.054595 0.001301 0.072758 0.139083
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 2.047284 0.019845 103.166 <2e-16 ***
## data$GenderMale -0.008617 0.024506 -0.352 0.726
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.09094 on 59 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.002091, Adjusted R-squared: -0.01482
## F-statistic: 0.1236 on 1 and 59 DF, p-value: 0.7264
##
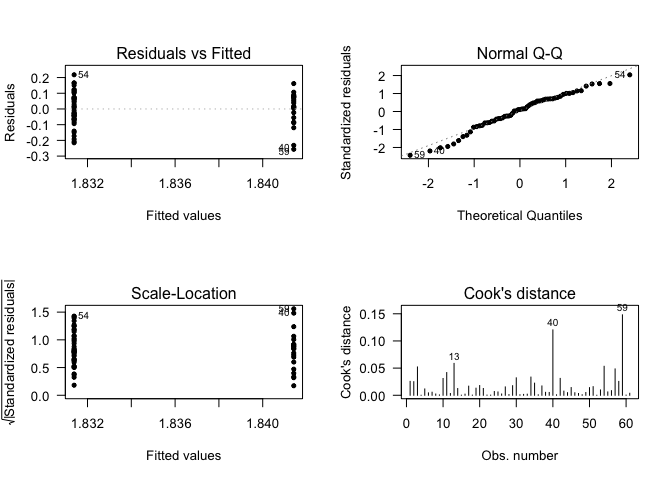
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$CLDN10 ~ data$Status)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.200394 -0.056033 0.002142 0.075311 0.124555
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 2.06200 0.01620 127.291 <2e-16 ***
## data$StatusHealthy control -0.04007 0.02272 -1.763 0.083 .
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.08873 on 59 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.05007, Adjusted R-squared: 0.03397
## F-statistic: 3.11 on 1 and 59 DF, p-value: 0.083
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$CLDN10 ~ data$Status + data$Gender)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.200894 -0.054854 0.001643 0.075772 0.124055
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 2.060819 0.021063 97.841 <2e-16 ***
## data$StatusHealthy control -0.040605 0.023690 -1.714 0.0919 .
## data$GenderMale 0.002211 0.024927 0.089 0.9296
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.08948 on 58 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.0502, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01745
## F-statistic: 1.533 on 2 and 58 DF, p-value: 0.2246
##
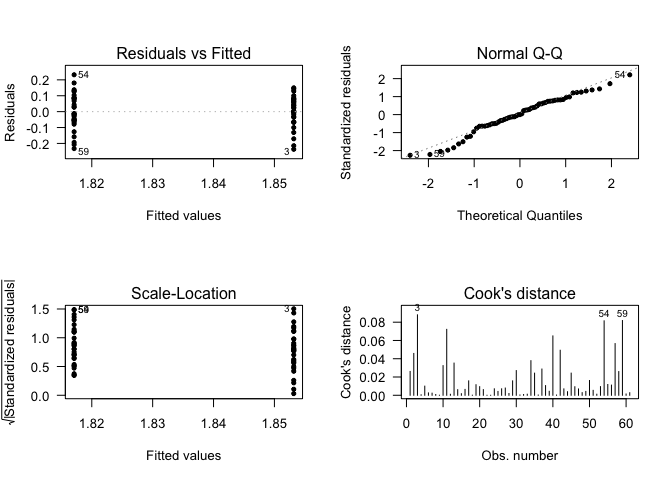
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$EFEMP1 ~ data$Gender)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.25679 -0.06492 0.01167 0.07423 0.21773
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 1.84142 0.02359 78.046 <2e-16 ***
## data$GenderMale -0.01003 0.02914 -0.344 0.732
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.1081 on 59 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.002004, Adjusted R-squared: -0.01491
## F-statistic: 0.1184 on 1 and 59 DF, p-value: 0.7319
##
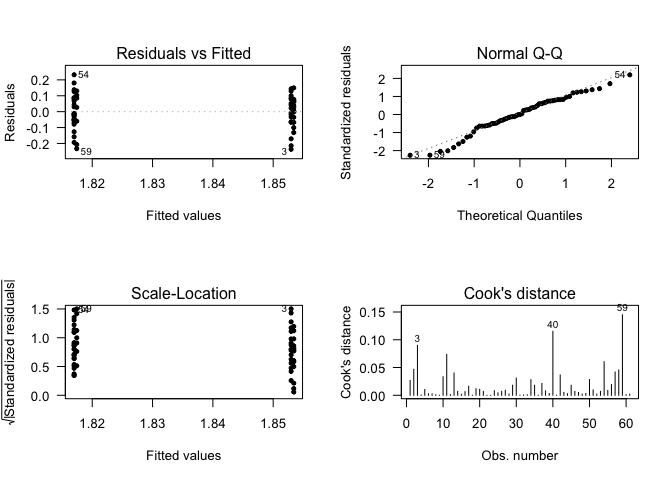
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$EFEMP1 ~ data$Status)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.237010 -0.059673 -0.000089 0.078471 0.232019
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 1.85318 0.01947 95.161 <2e-16 ***
## data$StatusHealthy control -0.03608 0.02732 -1.321 0.192
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.1067 on 59 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.02872, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01225
## F-statistic: 1.744 on 1 and 59 DF, p-value: 0.1917
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = data$EFEMP1 ~ data$Status + data$Gender)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -0.23681 -0.06001 -0.00032 0.07857 0.23212
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 1.8534086 0.0253228 73.191 <2e-16 ***
## data$StatusHealthy control -0.0359745 0.0284818 -1.263 0.212
## data$GenderMale -0.0004343 0.0299688 -0.014 0.988
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.1076 on 58 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.02872, Adjusted R-squared: -0.004773
## F-statistic: 0.8575 on 2 and 58 DF, p-value: 0.4295